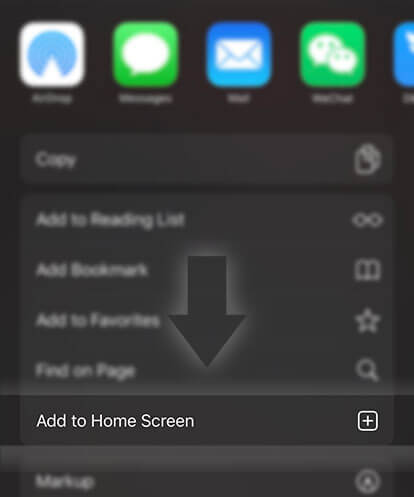
《IGCSE BIOLOGY》Topic 2
Advertisement
Topic 2 [Organisation of the Organism]
---
Cells are the of life, as all living organisms are made out of cells. Cells exist in various and . There are smaller components called within a cell and each organelle performs a inside the cell or for the cell.
:
- Also known as the .
- It is (Only allows some substances to pass through).
- The cell membrane is made of two layers. It had a (Love water) and a (Hate water) . Two layers of the head and tail connected together (Note that the tails are pointing towards each other) are called the .
:
between the cell and its' external environment
: (Only present in plant cells and fungus)
- A rigid layer surrounding the of .
- In fungus, the cell was is made of .
:
- To provide support and protection for the cell
- To prevent the cell from bursting in a dilute solution
:
- Between the and the .
- Containing organelles, salts, dissolved gases, nutrients, enzymes, and other organic molecules.
:
- Gives shape to the cell (Especially for animal cells, who do not have cell wall).
- Supports and protects the cell organelles
- Provides a medium for all to occur.
:
- Bound by the .
- Containing .
**The nucleus contains . The chromosomes contain .**
:
- Controls all cell activities
:
- Small, dot-like organelles found in large numbers in .
Two types of Ribosomes:
1. Attached to the .
2. Occur in the .
:
- To all types of .
:
- A flat, sealed sac of .
- attached on its' surface.
- Present in .
:
- and made by the ribosomes.
**Present in large amounts in cells that make proteins, such as gut cells.**
Advertisement
:
- A tubular sac of .
- Does not have ribosomes.
:
- and .
**Present in large amounts in cells that make lipids: e.g cells in the liver.**
: (Note that the plural of Mitochondrion is Mitochondria)
- Rod-shaped.
- Has an inner and outer membrane.
- 'The powerhouse of the cell'.
:
- Carry out (Refer to Topic 1 definition of respiration), which release in the form of .
- is a molecule that acts as a energy source/currency for the cell.
**Cells with high rates of metabolism have high numbers of mitochondria.**
: (Only present in plants)
- Containing , , or .
- Largest organelle in plant cells as they store water.
:
- For , , and .
: (Only present in plants)
- Have inner and outer membrane.
- Contain to trap energy from the sun.
:
- To carry out .
:
Animal Cells:
> Has NO cell walls, nucleus (in the middle of the cell), cytoplasm, NO chloroplast, NO vacuole, cell membrane.
> Stores food in the form of , which is made of a large number of glucose molecules binded together. Glycogen is stored in the .
Plant Cells:
> Has cell wall, nucleus (at the side of the cell), cytoplasm, chloroplast, vacuole, and cell membrane.
> Stores food in the form of , mostly in the .
:
:The basic structure and of a living organism.
: A group of with similar function working together to perform a .
:A structure made up of a group of working together to perform a .
: A group of with related functions, working together to perform .
: Different work together to make up one whole functional and complete multicellular organism.
By the process of .
- The cells become according to the functions they have to form.
Advertisement
- All cells are made in the , and they call start out as , which are cells with no specific function.
- Stem cells and become .
- Layer of tiny hairs: '', which move and push from one place to another.
- The mucus transports and traps dust and microbes in the trachea when pushed by the cilia.
- Conduct , which convey messages (Stimulus).
- Electrical impulses travel along a long fibre called the .
- A provides insulation for the nerve cell.
- There are many connections () at each end of the nerve cell to keep passing on the electrical impulse.
- A shape.
- Transport from the lungs to tissues for .
- The cytoplasm of red blood cell contains , a red pigment that carries oxygen.
- Matured red blood cells have to make more space for , so more oxygen can be transported.
- Very to pass through narrow blood vessels.
- Egg Cell (Aka. ), the .
- It is fertilised by a sperm cell to form a .
- Sperm Cell, the .
- They have a tail (flagellum) for swimming.
- They have a high amount of mitochondria to provide energy to swim and penetrate the ovum.
- and from the soil.
- Has (root hairs) to increase for absorption.
- and up the plant.
- so water can pass freely.
- as many cells have joined together to form a continuos tube.
- Wall strengthened by , a waterproof substance.
- The hollow space in the vessel is called the .
- The cells are , , and .
: (Magnification)
Magnification = Size of illustration / Actual size
1 cm = 10 mm
1 mm = 1000 µm
---
Advertisement
- End853 Chapters

Monster Pet Evolution
Three years ago, the animals and plants on Earth underwent crazy and unexplainable changes that included transformations, reversions, and the addition of otherworldly species. And it was the start of a brand-new type of profession in the new generation of humanity – Monster Trainers, people who specialized in taming monsters. On his 18th birthday, the protagonist of the story, Gao Peng, suddenly received the ability of being able to see the attribute data frame of monsters. With his ability, he aspired to become the strongest monster trainer that ever lived while looking for a method to revive his parents!
8 579 - In Serial35 Chapters

Tales of Astora: Insurrection
The second volume of the series "Tales of Astora". WARNING: since this is a direct sequel, it is necessary to read the first volume in order to understand the reference and the actual story. Link to the first novel: Tales of Astora: Legacy Following the events of the first volume, the Gods have found the hidden, mysterious world of Astora, now known as Valhalla and set out to destroy those who would defile the will of Multiverse. Behind the scene, an ancient force is about to make its first move after eons of slumber. Lead by the entities known as the Enders, they seek the destruction of the Gods and most of all, the world. Meanwhile, a tiny soul was born in a world of science where magic was but a myth. Plunged between the two camps, Astora, daughter of the Dark Lord, will soon face her destiny along with other peculiar beings she will meet in her journey.
8 201 - In Serial14 Chapters

The Journey of an Apprentice
The kingdom of Durnea is home to perhaps the largest of all the Great Towers, Draghiem. Within Draghiem's first floor rests Eisenrahm, the kingdom's capital city, and this is where our story begins. 17 year old Rygart Aren has dreamt of being the first to reach the top of Draghiem for as long as he can remember. Now that Rygart is confident in his ability he sets out to bring his dreams into reality! However, upon reaching his destination Rygart soon learns that dreams aren't near as much fun in reality as they are in the imagination. Just as Rygart is getting a grip on his new life things begin to change within Draghiem. Due the to actions of a careless adventurer events are set into motion that are sure to change the course of history, and not only for Durnea. Follow along as Rygart gets caught up in a storm of chaos that not only threatens to tear away his dreams, but also threatens the lives of everyone he cares about!
8 144 - In Serial7 Chapters

Pickle on the Nightmare Wall
She crawled out mines into squalid streets only to run into the bright fanged lights of the clubs to find the dustbowl trap that is the end of the world. Scraping a living in a forgotten corner of the world only defended for its dirt where people aren't people she survives. The wall of towers holding back the nightmares of the past where the warriors roam. Sure, most never come back, and few towers aren't run by the corps, church or tribes. One of the free towers will take her if she can pay. Gunther's Guns is the legend of old still holding back the tide. Maybe if she can survive the wall, she can hope for a better future, she has the capital to stake, but can she survive the world of shadows and iron. Join Pickle on the adventure to escape to a better life by descending into darkness.
8 190 - In Serial6 Chapters

Ouroborus
I was once a hero and this is about my reincarnation and my ordinary life and how i got summoned in another world as twist of fate to become a hero agian .-Would like you to comment so i can know my mistakes and better it THANK YOU
8 58 - In Serial50 Chapters

What Walks Among Us (currently being edited, will be posted by 2023)
Kodi has been locked away in her house since the whole apocalypse started. The thing is she's not sure whether the monster within the house is any better than the ones who've begun to take over the world one corpse at a time. Of course, how was she supposed to know the day the world ended was the same day her life would begin? #1 in Adventure#1 in Zombie
8 57







 Prev Chap
Prev Chap Next Chap
Next Chap Chap List
Chap List
 Boy
Boy Girl
Girl