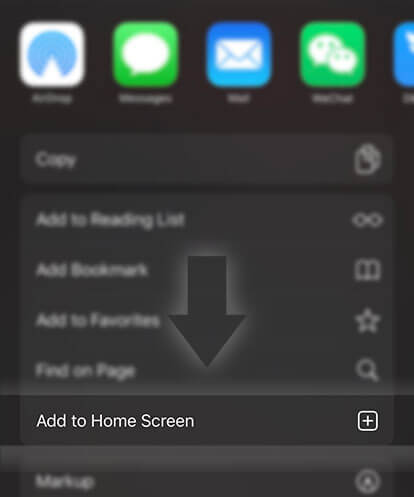
《Computer Engineering and Technology 1》Glossary
Advertisement
Access. To call up information out of storage
AI. See Artificial intelligence
Algorithm. A step-by-step procedure designed to solve a problem or achieve an objective
Alpha testing. First-stage testing of computer products, typically done in house by the developer. (Seealso Beta testing; Gamma testing.
Alphanumeric. Consisting of letters, numbers, and symbols
Antivirus software. A program designed to look for and destroy viruses that may infect the memory of a computer or files stored on a computer
Applet. A small application, that is, a program designed to perform a simple task. An applet is usually embedded within a larger program or downloaded from the Internet when needed
Application (or app). A program designed to perform information processing tasks for a specific purpose or activity (for example, desktop publishing and database management). (See also Applet; Killer app.
Archive. A file compressed for more efficient use of storage space. The compression of files may be accomplished by means of such programs as Stufflt
Artificial intelligence (AI). Computer systems that attempt to imitate human processes for analyzing and solving problems
Ascending sort. Sorting records from A to Z or 0 to 9. (See also Descending sort.
ASCII (pronounced as-kee). An acronym derived from American Standard Code for Information Interchange
ASCII is a standard 7-bit code that represents 128 characters. The use of this standard code permits computers made by different manufacturers to communicate with one another
B, b. B is the abbreviation of byte; b is the abbreviation of bit
Background printing. The ability of a computer to print a document while other work is being done on the keyboard and the display screen at the same time
Backup. Storage of duplicate files on disks, diskettes, or some other form of magnetic medium (such as tapes) as a safety measure in case the original medium is damaged or lost. (One word as a noun or an adjective: backup procedures; two words as a verb: back up your hard disk.
Bandwidth. The volume of information that a network can handle (usually expressed in bits per second). The greater the bandwidth, the more quickly data can be downloaded from the Internet or moved from a network to a user’s computer. The term bandwidth is now also used to refer to a person’s attention span (as in “Burt is a low-bandwidth kind of guy”) or a person’s ability to handle an assignment (as in “Sally lacks the bandwidth to do this job”). The question “How’s your bandwidth?” means “Are you busy?” Basic Input/Output System (BIOS). A set of programs stored in read-only memory (ROM) on IBM or IBM-compatible computers. These programs control the disk drives, the keyboard, and the display screen, and they handle start-up operations
BBS. See Bulletin board system
Beta testing. Second-stage testing of computer products, typically done by potential customers and outside experts to identify problems that need to be fixed before the product can be released for sale. (See also Alpha testing; Gamma Testing.
Binary code. The language used by computers in which data and instructions are represented by a series of 1s and 0s
Binary numbering system. A numbering system in which all numbers are represented by various combinations of the digits 0 and 1
BIOS. See Basic Input/Output System
Bit (b). An acronym derived from binary digit. The smallest unit of information that can be recognized by a computer. Bits are combined to represent characters. (See also Byte.
Bitmap. A method of storing a graphic image as a set of bits in a computer’s memory. To display the image on the screen, the computer converts the bits into pixels
Bits per second (bps). A measurement that describes the speed of data transmission between two pieces of equipment. (See also Transfer rate.
Advertisement
BlackBerry. A wireless palmtop computer that is especially helpful to business travelers. It permits users to send and receive e-mail and view other documents that they have on file. (See also Wi-Fi.
Blawg. See Blog
Bloatware. A program that uses an excessive amount of disk space and memory
Block. A segment of text that is selected so that it can be moved to another location or processed in some other way. (See also Block delete; Block move; Cut and paste.
Block delete. A command to delete (or erase) a segment of text
Block move. A command to reproduce a segment of text in another place and at the same time erase it from its original position. (See also Cut and paste.
Block protect. A command to prevent a page break from occurring within a block of text (for example, a table). (See also Orphan protection; Widow protection.
Blog. A blog (short for Web log) is an online diary in which an individual records and publishes his or her thoughts on one or more subjects. A blog devoted to legal matters is known as a blawg
Blogger. Someone who creates and maintains an online diary
Blogosphere. The complete set of blogs on the Internet
Bluetooth. A protocol that permits a wireless exchange of information between computers, cell phones, and other electronic devices within a radius of about 30 feet
Board. See Circuit board
Boilerplate. Standard wording (for example, sentences or paragraphs in form letters or clauses in legal documents) that is held in storage. When needed, it can be used as is, with minor modification, or in combination with new material to produce tailor-made documents
Bookmark list. See Favorites
Boot (short for bootstrap). To start a computer and load the operating system to prepare the computer to execute an application
Bozo filter. A program that screens out unwanted e-mail or other messages from individuals or organizations you no longer want to hear from
bps. See Bits per second
Bricks-and-clicks. Refers to a traditional business with a Web site. (See also Clicks-to-bricks.
Bricks-and-mortar. Refers to a traditional business that sells merchandise only in stores. (See also Clicks-and-mortar.
Brochureware. A product that is being actively marketed, even though the product is not yet (and may never be) ready for sale. (See also Vaporware.
Browser. See Web browser
Buffer. A holding area in memory that stores information temporarily. Also called cache
Bug. A software defect that causes a program to malfunction or cease to operate. Some writers now use bug to refer to hardware problems as well. (See also Debugging; Glitch.
Bulletin board system (BBS). An online information system, usually set up by an individual (called a system operator, or SYSOP) on a nonprofit basis for the enjoyment of other individuals with similar interests. (See also Internet.
Bundled software. Software that is sold along with a computer system; several software programs that are packaged together (also called software suites)
Burn. To record information on a disc such as a CD-R, a CD-RW, a DVD-R, or a DVD-RW
Bus. A pathway along which electronic signals travel between the components of a computer system
Button bar. See Toolbar
Byte (B). An acronym for binary term. The sequence of bits that represents a character. Each byte has 8 bits
Cache. See Buffer
Cancelbot (from cancel robot]. A program that detects spamming in newsgroups and automatically issues a cancel command. (See also Ham.
Card. See Circuit board; Adapter
Carpal tunnel syndrome. A wrist or hand injury caused by using a keyboard for long periods of time. A type of repetitive strain injury (RSI). (See also Mouse elbow.
Cathode-ray tube (CRT). See Display screen
Advertisement
CD-R. Compact disc-recordable
CD-ROM (pronounced cee-dee-rom). An acronym derived from compact disc-read-only memory. A form of optical storage. One compact disc can hold up to 250,000 text pages; it can also be used to store graphics, sound, and video. (See also DVD-ROM.
CD-RW. Compact disc-rewritable
Cell. A box or rectangle within a table or spreadsheet where a column and a row intersect; an area in which information can be entered in the form of text or figures
Central processing unit (CPU). The brains of an information processing system; the processing component that controls the interpretation and execution of instructions. (See also Motherboard.
Character. A single letter, figure, punctuation mark, or symbol produced by a keystroke on a computer
Each character is represented by a byte
Character set. The complete set of characters—alphabetic, numeric, and symbolic—displayable on a computer. (see also ASCII.
Character string. A specified sequence of typed characters, usually representing a word or phrase. A character string is often used to locate a particular word or phrase wherever it appears in a document so that it can be automatically replaced with another word or phrase. If a person’s name has been consistently misspelled or a date appears incorrectly in several places, the error can be easily corrected. (See also Search and replace.
Characters per inch (cpi). The number of characters in a fixed-pitch font that will fit within 1 inch
Characters per second (cps). The number of characters printed in 1 second; a measurement frequently used to describe the speed of a printer
Chat. A method of communication in which people type text messages to each other, thereby holding a conversation over a network such as the Internet. (See also Newsgroup.
Check box. A small box that appears onscreen alongside each option displayed in a dialog box. When an option is selected, an X or a check mark appears inside the box
Chip. An integrated circuit used in computers
Chip jewelry. An obsolete computer
Circuit board. A board or card that carries the necessary electronic components for a particular computer function (for example, memory). The circuit boards that come with the original equipment perform the standard functions identified with that type of equipment. Additional circuit boards expand the kinds of functions that the equipment can perform. Also called a board, a card, or an expansion board
Clear. A command to erase information
Click. To quickly press and release a mouse button once while the cursor (mouse pointer) is positioned over a specific item on the screen. (See also Double-click.
Clicks-and-mortar. Refers to a business that sells merchandise online as well as in stores. (See also Bricks-and-mortar.
Clicks-to-bricks. Refers to an Internet company that opens stores. (See also Bricks-and-clicks.
Client/server computing. A network of computers that consists of a file server (a computer that runs a database management system) and individual clients (computers that request and process data obtained from the file server)
Clipboard. A holding area in memory where information that has been copied or cut (text, graphics, sound, or video) can be stored until the information is inserted elsewhere. (See also Copy; Cut; Cut and paste.
Column. A vertical block of cells in a table or spreadsheet. (See also Row.
Command. An instruction that causes a program or computer to perform a function. A command may be given by means of a special keystroke (or series of keystrokes), or the command may be chosen from a menu
Commercial online service. See Internet service provider
Compatibility. The ability of one type of computer, device, data file, or program to share information or to communicate with another. (See also ASCII.
Computer. An electronic device that is capable of (1) accepting, storing, and logically manipulating data or text that is input and (2) processing and producing output (results or decisions) on the basis of stored programs of instructions. Some computers are also capable of processing graphics, video, and voice input. Most computers include a keyboard for text entry, a central processing unit, one or more disk drives, a display screen, and a printer—components referred to as hardware
Control menu. An onscreen Windows element that appears in a box in the upper left corner of a window. The control menu allows the user the option of adjusting the size of the window, closing or reopening the window, or switching to another window
Cookie. A small text file that a Web server stores on a user’s hard drive when the user visits certain Web sites. A cookie contains all the information that a user has to submit on a first visit to a particular Web site in order to gain access. When a user revisits that Web site, the cookie makes it unnecessary for the user to enter the same information all over again. The positive aspect of cookies is that they make it possible for users to take advantage of the convenient “shopping cart” feature of many Web sites. Unfortunately, cookies also make it possible for marketing organizations to monitor users’ browsing patterns; users then find themselves the targets of custom-tailored marketing campaigns
Copy. To reproduce information elsewhere. The original information remains in place. (See also Cut.
cpi. See Characters per inch
cps. See Characters per second
CPU. See Central processing unit
Cracker. The preferred term (rather than hacker) used to refer to a computer criminal who penetrates a computer to steal information or damage the program in some way
Crash. A malfunction in hardware or software that keeps a computer from functioning. (See also Bug; Glitch.
CRT. Cathode-ray tube. (See also Display screen.
Cursor. A special character (usually a blinking underline, dot, or vertical line) that indicates where the next typed character will appear on the display screen. Also known as the mouse pointer (arrow) or I-beam pointer. Microsoft Word refers to the cursor as the insertion point. (See also Prompt.
Cursor positioning. The movement of the cursor on the display screen. Most computers have four keys to control up, down, left, and right movement. Many computers also permit the use of a mouse to position the cursor
Cut. To remove text from its original location and place it on a clipboard. (See also Copy; Paste.
Cut and paste. To move a block of text from one place to another
Cyberspace. A realistic simulation of a three-dimensional world created by a computer system; also referred to as virtual reality. Now commonly used to refer to the world of the Internet as a whole
Cybersquatting. Registering a potentially valuable Internet address in the hope of selling it at a profit later on to an organization for which this address would be ideal
Cybrarian. The electronic equivalent of a librarian. A person who makes a career of online research and data retrieval
Data. Information consisting of letters, numbers, symbols, sound, or images—in a form that can be processed by a computer
Data compression. A procedure for reducing the volume of data so as to shorten the time needed to transfer the data or to reduce the amount of space needed to store the data
Database. A stored collection of information
Database management system (DBMS). The software needed to establish and maintain a database and manage the-stored information
DDE. See Dynamic data exchange
Dead-tree edition. The paper version of a publication available online
Debugging. Locating and eliminating defects in a program. (See also Bug.
Decimal tab. A type of tab that aligns columns of figures on the decimal point
Default settings. The preestablished settings (for margins, font, type size, tab stops, and so on) that a program will follow unless the user changes them
Delete. A command to erase information in storage
Denial of service (DoS) attack. A malicious act intended to shut down a Web site or a network by flooding it with too much information. Users who attempt to visit the site will be denied access
Descending sort. Sorting records from Z to A or 9 to 0. (See also Ascending sort.
Desktop. The electronic work area on a display screen
Desktop computer. A microcomputer that is bigger than a laptop
Desktop publishing (DTP). A system that processes the text and graphics and, by means of page layout software and a laser printer, produces high-quality pages suitable for printing or in-house reproduction
Dialog box. A message box on the screen that supplies information to—or requests information from— the user
Dictionary. A program used to check the spelling of each word entered in the computer
Digerati. A term referring to the elite group of intellectuals in the computer world (in the same way that literati refers to the elite group of intellectuals in the literary world)
Directory. A list of the files stored on a disk
Disc. A nonmagnetic storage medium that is used in conjunction with optical technology. (See also CD-ROM.
Disk. A random-access, magnetically coated storage medium used to store and retrieve information
(See also Diskette; Hard disk.
Disk drive. The component of a computer into which a disk is inserted so that it can be read or written on
Disk operating system. See DOS
Diskette. A small, nonrigid disk with limited storage capacity. Also known as a floppy disk
Display screen. A device similar to a television screen and used on a computer to display text and graphics. Also called a video display terminal (VDT) or a monitor
Distributed processing system. A form of a local area network in which each user has a fully functional computer but all users can share data and application software. The data and software are distributed among the linked computers and not stored in one central computer
Document. Any printed business communication—for example, a letter, memo, report, table, or form(See also File.
Documentation. The manuals or guides distributed with hardware or software
Domain. Typically, a three-letter element in a Web address or an e-mail address. The domain— commonly referred to as the zone—indicates the type of organization that owns the computer being identified in the address. For example, .com signifies a commercial organization; .edu signifies an educational institution. (See ¶1508b for a list of the most common domains.
DOS (pronounced dahs or doss). An acronym derived from disk operating system. The term refers to a program that allows the computer to manage the storage of information on disks and controls other aspects of a computer’s operation
DoS (pronounced dee-oh-ess). See Denial of service attack. (Note the differences in spelling and pronunciation between DOS and DoS.
Dot. The period symbol used in e-mail and Web addresses. Always referred to as a dot (never as a period). Thus the domain name aol.com would be pronounced ay-oh-ell-dot-com. Internet surfers who spend a lot of time in the .com domain are sometimes referred to as dot communists
Dot-com. An organization that sells its products or services on a Web site (with a URL endng in .com)
A dot-com that fails to stay in business is referred to as a dot-bomb
Dot matrix printer. A printer that uses pins to produce characters made up of small dots. This kind of printer is generally used by organizations that want to produce form letters or mailing labels economically
Advertisement
- In Serial12 Chapters

Stratus Online: Awakening
Edwin Morris has been playing Sakarn Online almost his whole life, in fact, most people have. While he considers himself a skilled player, he never could really find the time to take his game to the next level and pay the bills. After he is finally pushed over the edge with his job at Burger Planet, Edwin stumbles upon a man representing a game company called Stratus Labs. Edwin is offered a lucrative position within the company to test and beat Stratus Online, an incredible, fully-immersive MMO designed to dethrone Sakarn Online. Edwin will have to unite with his friends and compete against other teams, but not everything is as it seems within Stratus Labs and the stakes are much higher than he could have ever imagined. With the clock ticking, will Edwin have what it takes to complete the seemingly insurmountable task of beating Stratus Online before it's too late?
8 180 - In Serial40 Chapters

The Forsakens
In Chicken's Head academy, there are lists of many things. One of them is the list of people to stay away from. This is the story of such people that are forsaken. Cover made by CookieJiyen.
8 415 - In Serial7 Chapters

Milky Way: Story of Eden
In the year 5016, THE MILKY WAY FEDERATION has expanded research facilities and space colonies throughout the Galaxy. The dastardly ABRENO REGIME has sent spies into Federation Controlled science facilities in deep space. On the edge of the Vakkaro Star System, a lowly dwarf star gives light to a single small ice planet. This solar system is restricted allowing only FEDERATION ships to enter. On the small planet of FC-1293-Keta, resides a large science base for the INTERGALACTIC SOCIETY OF SCIENCE dubbed THE EDEN SCIENCE COLONY by the organization.While the possibility of a spy is low, tensions are high. Scientists work every hour in this colony on advanced experiments in order to better life in the Galaxy and for THE FEDERATION.
8 87 - In Serial47 Chapters

The Assassin's Mate
Darshana Cameron is 19 years old. She was taken at the age 7, by a group of rogues. they took her captive and tortured her for 6 years. She found the courage to escape and bumped into a man called Derek, who took her in as his family and trained her for three years. She joins an agency at the age of 16 and has been working as an assassin for 3years. what happens when her agency sends her out to the field to capture a certain drug gang whom she thought were human but are werewolves. What happens when she meets her mate on that same day? Will she learn to love him and give in to him or will she return to her old ways as an assassin?
8 180 - In Serial21 Chapters

Radiant (Lashton)
"Calum, he's just so...radiant""No shit Luke, you stare at him like he's the freaking sun"***The one where Ashton's just so radiant, and Luke can't help but fall for him, but Ashton has secrets and Luke has a girlfriend.#22- Lashton
8 111 - In Serial30 Chapters

Broken-(A Loki Fanfic)
Lilith's life changes completely when she becomes a Valkyrie. And then it changes even more when she becomes Loki's Valkyrie. She's told that he's pure evil and to stay away from him. But when everyone else wants her dead, where else can she go? (Loki or any of the other Marvel characters do not belong to me. They are property of Marvel. The story takes place during Thor: the Dark World.)(TRIGGER WARNING: This series will have heavy mentions of self harm. It is not meant to glorify self harm at all, but be weary while reading it.)
8 180







 Prev Chap
Prev Chap Next Chap
Next Chap Chap List
Chap List
 Boy
Boy Girl
Girl